The IIS Chip Gallery
Dross (2009)
by

| Application | Cryptography |
| Technology | 90 |
| Manufacturer | UMC |
| Type | Diploma Thesis |
| Package | QFN56 |
| Dimensions | 1875μm x 1875μm |
| Gates | 350 kGE |
| Voltage | 1.2 V |
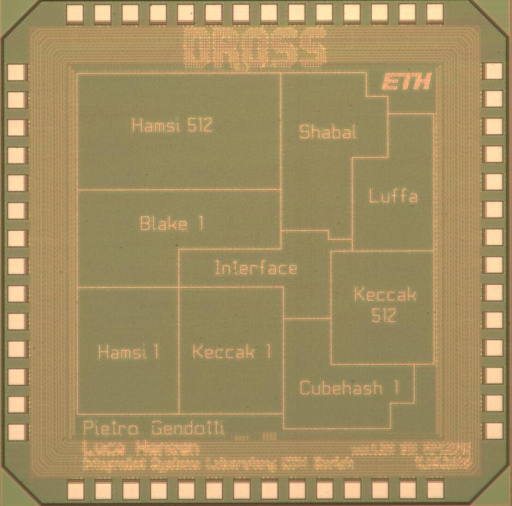
During this diploma thesis, ten different architectures of the six non-AES-based SHA-3 candidates BLAKE, Cube- Hash, Hamsi, Keccak, Luffa and Shabal have been investigated and implemented in VHDL. The decision to take into account only candidates that are not based on the AES block cipher, exlcuding even those using only some steps of it, is mainly due to the fact that AES has already been deeply analyzed both in software and in hardware.
Among the investigated candidates, Keccak and Luffa, are the two algorithms that have shown the best performance, both in terms of area occupation and computational speed. The reason is their simple and compact implementation. In addition, most of the architectures implemented have shown appreciable performance in comparison with other researchers' implementations.
As a proof of concept, eight different architectures have been implemented on a 90 nm CMOS ASIC called DROSS. The chip, including the seal ring, has a fixed size of 1.925 mm x 1.925 mm, which limits the logical complexity to approximately 450'000 gate equivalents. The design uses a special-purpose interface to test the algorithms. In total, three clock domains have been specified at 300, 500 and 700 MHz in order to get optimal conditions for each algorithm.
For related results see also The SHA3 Hardware Evaluation WWW site.